Social Media and its impact on Healthcare:
Social media has revolutionized how we connect and communicate, transforming various industries, including healthcare. Online communities on social media platforms have become powerful tools for healthcare professionals, organizations, and medical training. In this blog, we will explore the profound impact of social media on healthcare and how it leverages the power of online communities. We will also discuss the essential role of medical manikins in healthcare training and how SEM Trainers can serve as a one-stop shop for medical simulation needs.
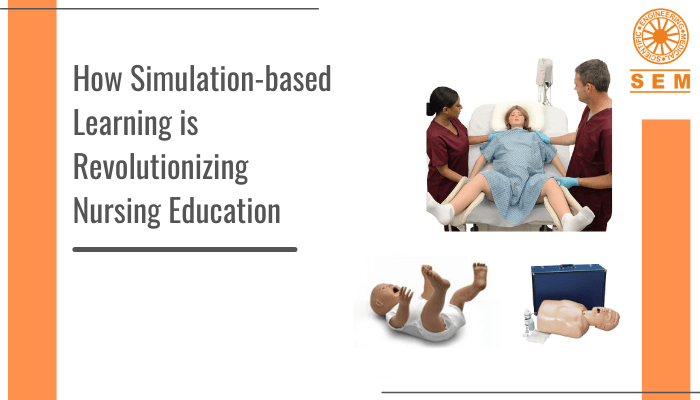
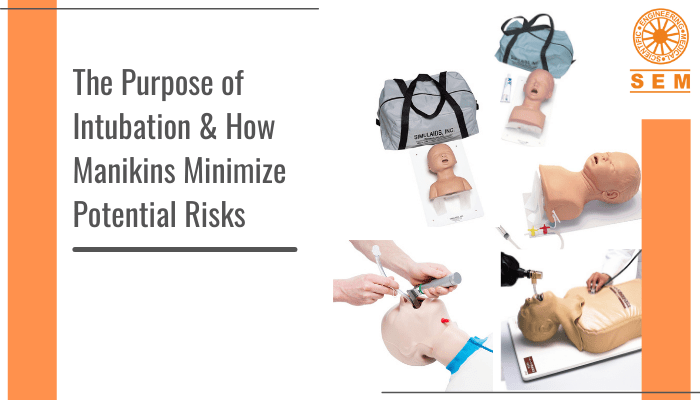
Building Awareness and Education: Social media platforms provide an extensive reach, making them effective channels for raising awareness about health conditions and diseases. Healthcare organizations, medical professionals, and medical manikin websites can utilize social media to share valuable information, articles, infographics, and videos. By incorporating SEO-friendly keywords and relevant hashtags, they can ensure their content reaches the intended audience. This not only helps people understand their health better but also promotes preventive measures, early diagnosis, and access to appropriate treatments. Through social media, medical manikin websites like us at SEM Trainers can educate healthcare professionals and students about the importance of practical training with lifelike simulators.
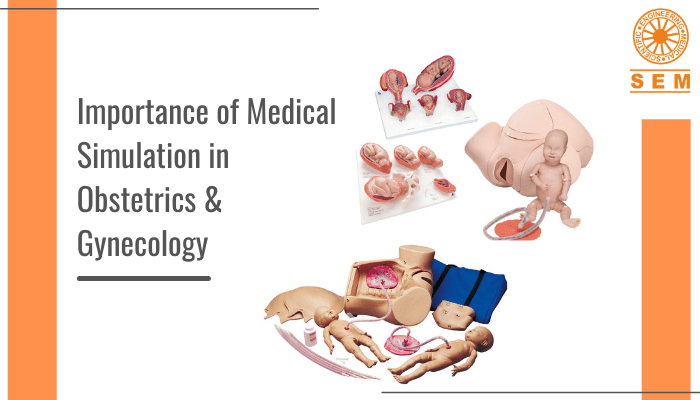
Patient Support and Empowerment: Social media has created online communities where patients can connect, share experiences, and find support. This is particularly significant for individuals living with chronic illnesses, rare diseases, or mental health conditions who often feel isolated. Social media platforms provide a safe space for patients to ask questions, seek advice, and exchange emotional support with others facing similar challenges. Medical manikin websites can leverage social media to contribute to these communities by sharing resources, training tips, and success stories of healthcare professionals using simulators to improve patient care. By doing so, they empower patients to become advocates for their own health while emphasizing the importance of practical training with medical manikins.
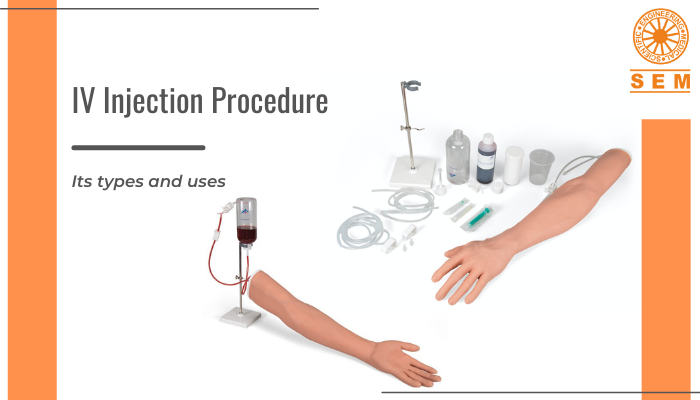
Real-time Communication and Feedback: Social media platforms enable instant communication between healthcare providers, patients, and the general public. This real-time interaction allows medical professionals to address queries, provide accurate information, and debunk misinformation promptly. Patients can connect with healthcare providers directly, reducing barriers to access and fostering a patient-centered approach. Furthermore, social media serves as a valuable tool for gathering feedback and insights from patients, which can help medical manikin websites like us at SEM Trainers to enhance our simulators’ features and tailor our products to meet the needs of healthcare professionals and students effectively.
Research and Data Collection: The vast amount of data generated on social media platforms presents an immense opportunity for healthcare research. By analyzing trends, discussions, and sentiments, researchers can gain valuable insights into public health concerns, emerging diseases, and treatment outcomes. Social media data can help identify patterns, track disease outbreaks, and contribute to epidemiological studies. Additionally, we can utilize social media surveys and polls to gather data quickly and efficiently. This valuable information can be used to understand the training needs of healthcare professionals, improve medical manikin design, and advance medical simulation techniques for better patient outcomes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103576/
To unlock the full potential of healthcare training, explore the comprehensive range of medical manikins and simulation solutions available at SEM Trainers today. As a one-stop shop for medical simulation needs, SEM Trainers offer a wide range of high-quality medical manikins and simulation equipment. https://www.semtrainers.com/contact-us