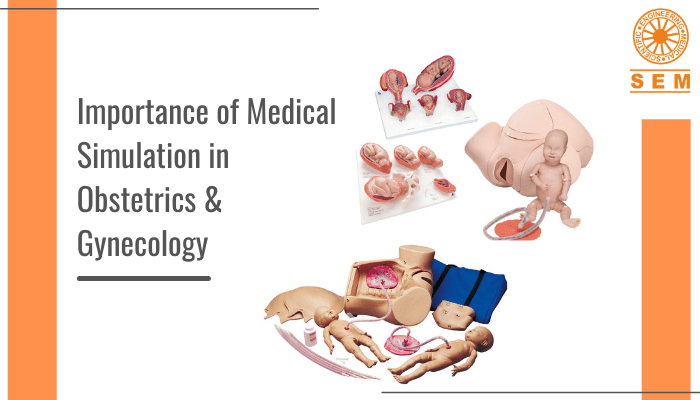
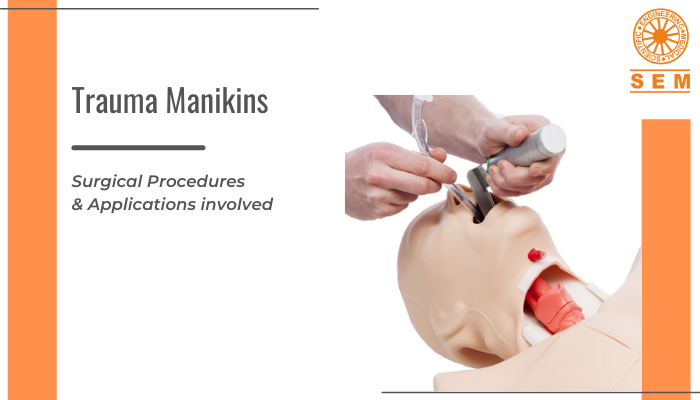
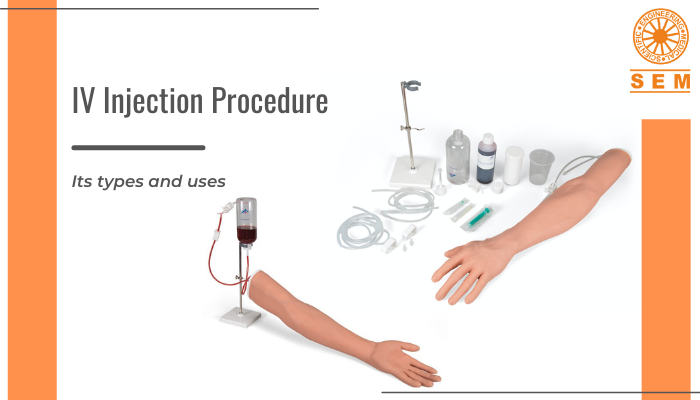
Medical Simulation Training: Market Share, Projected Growth
Over the years, we have recognized the potential of using simulation training to further the state of the global healthcare system. With recent technological advancements, simulators have not only started gaining recognition and acceptance, but are starting to become the norm. Numerous researches have been carried out to predict where medical simulation training will reach by the year 2030.
Expected Market Growth by 2030
In 2020, the global medical simulation market was valued at $1,687.5 million- this is the total product and service sales revenue it totalled in that entire year. In 2021, this was $1.8 billion. And this is growing at a compound annual growth rate of 13.9% as of 2021. And by 2028, this rate could reach anywhere from 14.4% to 16.3%. So, the market is projected to reach $6,688.6 million by 2030. That is almost 6.7 billion dollars! Even within the medical simulation market, the market share of models and simulators is the highest of all the products and services available.
What is driving the growth of the medical simulation market?
As technology advances and we create a better global healthcare system for ourselves, we see a rise in the growth of medical simulation devices in our hospitals and our medical and nursing education systems or facilities. We have observed a series of rapid advancements in healthcare technologies over the last few decades, and continue to do so with technologies like Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, 3D printing, and nanotechnology, and these will continue to shape the future of healthcare for years to come. And given how a number of invasive techniques are starting to become the standard for many surgical procedures, this is further driving the market growth of medical simulation as there is a need for skilled professionals to perform surgeries like laparoscopy.
We are really starting to adopt medical simulation
A major factor for the adoption of medical simulation is the frequency of medical errors that happen globally. Statistically, around 5.2 million medical errors happen every year in India. Of these, around 98,000 people die – every year, due to medical negligence and mistakes. With the quality of technology we have at our disposal today, that is just not acceptable. There is an urgent need to identify and remedy this. Reducing medical errors not only results in saving lives, but it also reduces administration errors, preparation errors, and overall costs.
The difference that simulation training makes
It has been proved research after research that simulators and manikins have been playing an indispensable role in how we approach healthcare and how we train the next generation of medical and nursing professionals each time. Simulation is the only teaching method able to provide repeated hands-on experience with real-time feedback in a safe, controlled environment- without causing any harm or inconvenience to real patients. It creates a forgiving environment that not only lets learners make mistakes and learn from them, but because they have the permission to make mistakes, it gives them the freedom to look around and play with all the features and controls. It enables generations of aspirants to become skilled and capable enough before transitioning to the real clinical setting; it makes them competent enough to do that. This, in turn, also reduces healthcare costs. Additionally, the enhancement of clinical competence further fuels the market growth of the medical simulation market.
Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Growth Rate of Medical Simulation Training
As the pandemic unraveled in the last few months of 2020, with border restrictions and the ongoing healthcare crisis, the focus was predominantly on handling acute operational demands instead of on addressing training needs. The growth rate observed was only 1.5% as compared to the projected growth rate of 9.2% predicted before the pandemic.
Key Challenges Affecting the Demand for Medical Simulation
There is a communication and skill gap between simulation experts and clinical staff. Additionally, for a clinical skills lab to be successful, it is important to have the necessary amount of clinical staff skilled at running a simulation lab, handling the simulators, and being able to execute simulation scenarios that are accompanied by debriefing. Another challenge is the inability to deal with the problems posed by unreliable wireless connectivity in wireless simulators.
Things are really starting to pace up after the pandemic for the medical simulation industry. What the future holds for the industry will certainly be interesting to watch.