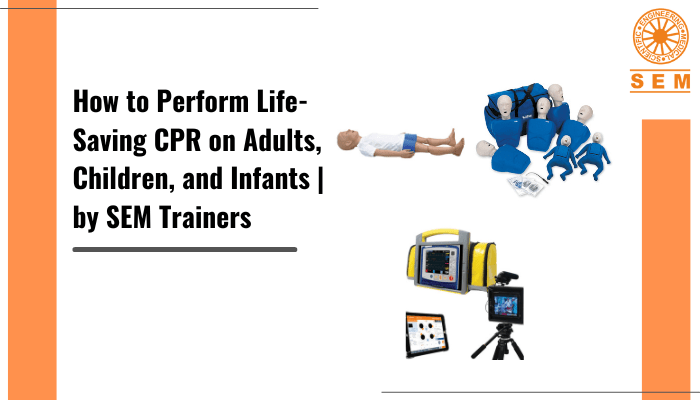
How to Perform Life-Saving CPR on Adults, Children, and Infants | by SEM Trainers
When most people talk about learning life-saving CPR, they either think they won’t be able to do it or wonder if they’ll ever really be in that situation. But did you know that around 45% of cardiac arrest victims are saved because a bystander did CPR on them?
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure and a first-aid, life-saving skill that can restore breathing and heartbeat in someone who has gone into cardiac arrest and isn’t breathing properly. Whether it’s from a heart attack, near-drowning, or other causes, CPR can save a life using procedures like chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth breathing. While this doesn’t mean that someone saved with CPR will magically be treated, CPR can keep blood flowing and keep the brain and other organs till medical help arrives.
The thing is- you don’t need to be a health professional to do CPR, anyone can learn to do it. By learning life-saving CPR, you can not only save the life of a stranger some day, but also of a friend or family member.
How to do Chest Compressions
- Lay the patient on their back, kneeling next to them.
- Put the heel of your hand on their chest- in the center of the lower half of the breastbone. Put your other hand on top of the first and interlock your fingers.
- Bring yourself above the patient’s chest, and with straight arms, use your body weight to press down on their chest by 1/3 of their chest depth.
- Release the pressure. One compression is complete.
How to give Mouth-to-Mouth
- Put one hand on their forehead and the other under their chin to open their airway.
- Use one hand to pinch their nose closed, and the other to open their mouth.
- Now, take a breath in and, placing your lips on theirs to create a seal, blow into their mouth for 1 second and watch the chest rise. After the breath, watch the chest fall, and listen and feel for the air being expelled.
- Then, take another breath and repeat.
If the chest does not rise, check the mouth for any blockages and remove them. The head should be tilted and no air should be leaking out from your mouth to theirs.
In 2 minutes, you should give 5 sets of 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths for each set. If you’re only doing compressions, do 100-120 compressions per minute. Although, alternating between compressions and breaths can help you do it longer.
Keep doing this till help arrives, you get exhausted, or the patient starts coughing, talking, breathing normally, or moving again- then put them in the recovery position.
How to do CPR on an Adult
- First, check if the scene is safe to help. Don’t put yourself or others in danger.
- Now, look for a response from the patient- loudly ask their name and squeeze their shoulder.
- If they don’t respond, call 108 or ask someone else to call, but don’t leave the patient alone.
- Check if their mouth and throat are clear and remove blockages like vomit, blood, or food. Tilt their head back and lift their chin.
- Check their breathing. Even if the patient is breathing properly, stay with them till help arrives. If they’re not breathing properly, start chest compressions immediately using both hands.
- Attach a defibrillator, if available.
How to do CPR on a Child
The process of giving CPR to a child is almost the same as that for an adult. The only difference here is that you’ll probably do the compressions with one hand instead of 2 if the child’s chest is too small for 2 hands.
How to do CPR on an Infant
For babies less than 1 year old, the process is almost the same as that for an adult or a child. There are a few differences, like when checking for a response from the baby, you shouldn’t shake them as it can cause shaken baby syndrome, and ultimately, even death. Also, for infants, you’ll do the compressions with only 2 fingers. And for mouth-to-mouth, you’ll need to tilt their head back very slightly and lift their chin without resting your hands on their throat before taking a breath in and covering their mouth and nose with your mouth and blowing for 1 second. You’ll watch the chest rise, and then you’ll watch the chest fall after the breath, and listen and feel for signs of air being expelled.
You really don’t need to be a doctor or a medical professional to be able to do CPR on someone and save a life. The key is to start as soon as you can.
More Blog:
How to use the 3b Scientific p90 Birthing Simulator by SEM Trainers?
Follow us on Social Media :