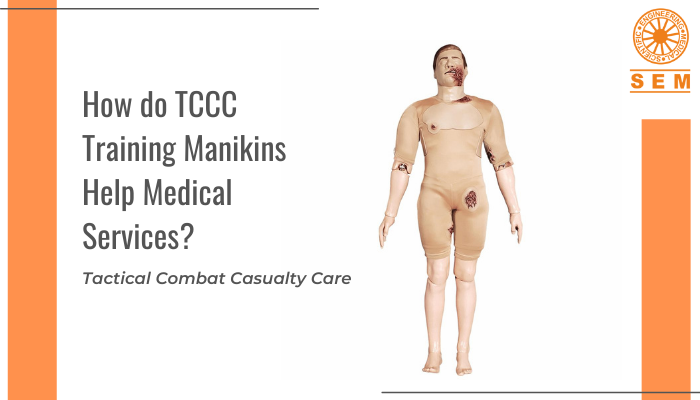
Top 10 Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) Medical Simulators You’ll Need | SEM Trainers
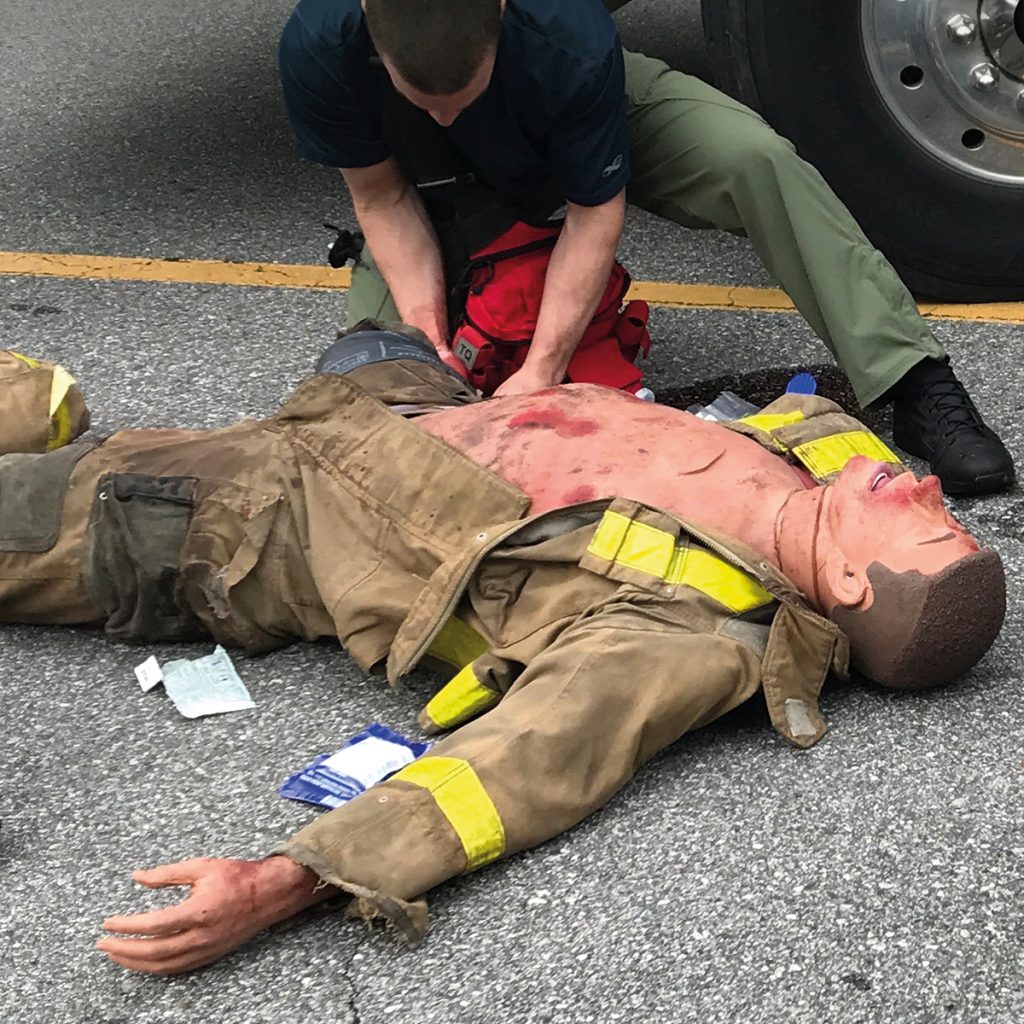
Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) are guidelines for providing immediate medical care for life-threatening injuries on the battlefield. Training for TCCC skills can be provided in 3 phases (care under fire, tactical field care, and tactical evaluation care). Students learn the management of trauma care and blast related injuries, and handle hemorrhage control and airway management. Learners cannot be assigned to real patients for handling traumatic combat injuries, but with the help of hyper-realistic simulators, they get all the practice they might need!
Here are some of our powerful TCCC simulators:
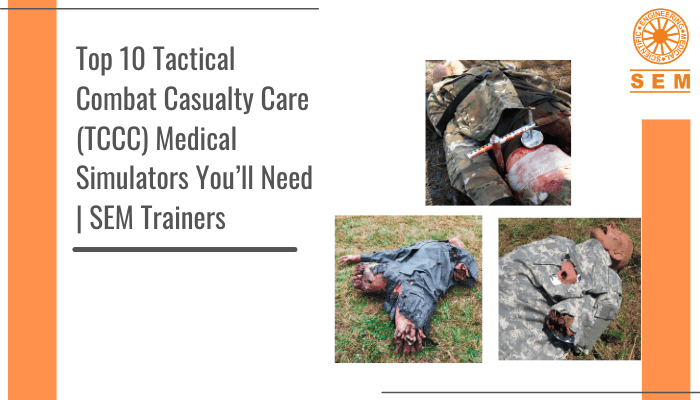
The three most preventable causes of death are massive bleeding, airway obstruction, and tension pneumothorax. This one is a hyper-realistic full-body manikin that is perfect for training on the procedures that treat these 3 conditions. This manikin holds 3-4 liters of blood and simulates a 2-3 psi blood pressure.
This full-body simulator is great for realistically training combat trauma care for major vascular injuries for hemorrhage management and airway control using common wound patterns of combat. Durable in the toughest training scenarios, this simulator is water resistant and great for indoor and outdoor training for the military, government forces, medical rescue, and private security. It is remote-controlled and simple to operate, and comes with an instructor interface tablet with simulation logs and self-diagnosis. Use it for high threat extraction training and realistic TCCC field training scenarios.
A full-body TCCC simulator for training combat trauma care for traumatic amputation injuries that are above the left elbow and above the left knee along with an amputation at the upper right thigh above the tourniquet line. Highly durable in the toughest training scenarios and water resistant, this simulator is great for indoor and outdoor training. With its lifelike tissue, it is great for training of hemorrhage management and airway control, high threat extraction training, and realistic TCCC field training scenarios.
This full-body simulator is great for training for multiple traumatic gunshot wounds (like sucking chest wounds) and amputation injuries above the left elbow and the left knee. Like the others, this is highly durable and water resistant, and great for training of hemorrhage management, airway control, high threat extraction training, and realistic TCCC field training scenarios.
A full-body simulator good for training combat trauma care for abdominal wounds with evisceration and a traumatic amputation above the right wrist. Highly durable and water resistant, and great for external hemorrhage and airway control, high threat extraction training, and realistic TCCC field training scenarios.
Another full-body TCCC simulator for combat trauma care training of gunshot wound management, hemorrhage management, airway management, and trauma management related to the casualty’s breathing and circulation. Highly durable and water resistant, and great for hemorrhage management, airway control, high threat extraction training, and realistic TCCC field training scenarios.
This one is a full-sized, remotely-activated simulator for point-of-injury, tactical medicine training for law enforcement and first responders. With realistic and anatomically-accurate soft tissue, durability, and water resistance, this simulator has remotely-activated pulsatile bleeding, multiple injuries like gunshot wounds, stab wounds, and crushing injuries, and an amputation on the left leg above the knee for tourniquet application.
This one is a CPR module with detailed real-time visual feedback on CPR quality. A sensor keeps track of the rate, depth, and release of each compression, and the system evaluates CPR time, correct chest compressions, pressure depth status bar, pressure posture, and pressure CPR rhythm. The system can be worn on the wrist, deployed on a manikin, or even placed inside a manikin.
A trainer for hemorrhage control on the upper extremity with realistic wound and bleeding simulation. Affordable and great for training of bleeding control and management of traumatic arm injuries. It has a deep laceration/stab wound, a large caliber gunshot wound, and a junctional wound in the shoulder.
A patient monitor that is a smart, integrated, and modular simulation ecosystem and lets medical educators run multiple scenarios – from basic to sophisticated. It is mobile, so you can conduct training anywhere- whether it’s an ambulance, a helicopter, a hospital, or a skills lab.
For meticulous tactical combat casualty care training with the help of simulators, call us at 02632 257259 or drop us a mail at sem@semtrainers.com today!