How is Behaviorism Applied in Medical Simulation?
Research has time and again proved the effectiveness of the use of simulation in medical training. And because it is so expensive with so many costs factoring in, it is important to make it more effective in what it does. Since learning is the goal of simulation-led training, one way to do this is to integrate learning theories into the process. In this blog, we will talk about how behaviorism is applied in medical simulation to increase its efficiency.

What is Behaviorism?
Everyone learns differently- we all have different learning styles. Learning theories are concerned with how we learn, process, and remember. One such learning theory is behaviorism, a theory that suggests that all learning is acquired through conditions. Learning (behavior) is either a reflex to an environmental stimulus or a consequence of our history. Learning happens when connections are made between environmental stimuli and a person’s responses that follow. So when we manipulate the stimuli, we can alter behavior through learning.
So how does this apply to learning?
We can make use of the concept of behaviorism and the consequences of behavior by encouraging learning through reinforcement and punishment (both positive and negative). As suggested by operant conditioning, a response is controlled by its consequence. With strategies like positive reinforcement, responding to an action with a desirable consequence can create a positive association and encourage repetition of the action. When learners repeatedly practice critical skills in a safe simulation environment, they learn and remember better. Also, when the instructor gives him immediate feedback- whether it’s a reinforcement or a punishment, it drives operant conditioning and changes his response. So, reinforcement will encourage him to make the right choice again, and punishment will discourage him from making the wrong choice the next time. Another technique is systematic desensitization, in which fear and anxiety are reduced by repeated exposure (because fear is learned, it can be unlearned).
How to apply behaviorism to medical simulation?
Here are a few things you can do to improve the learning experience:
- Simulation runs better when you have prepared everything in advance. If you can design a simulation focusing on a specific psychomotor skill, while cutting out distractions and other factors, you will be utilizing the principles of behaviorism. As cognitive demand will decrease, the learner will be able to completely focus on the one skill, and the instructor will be able to measure results directly.
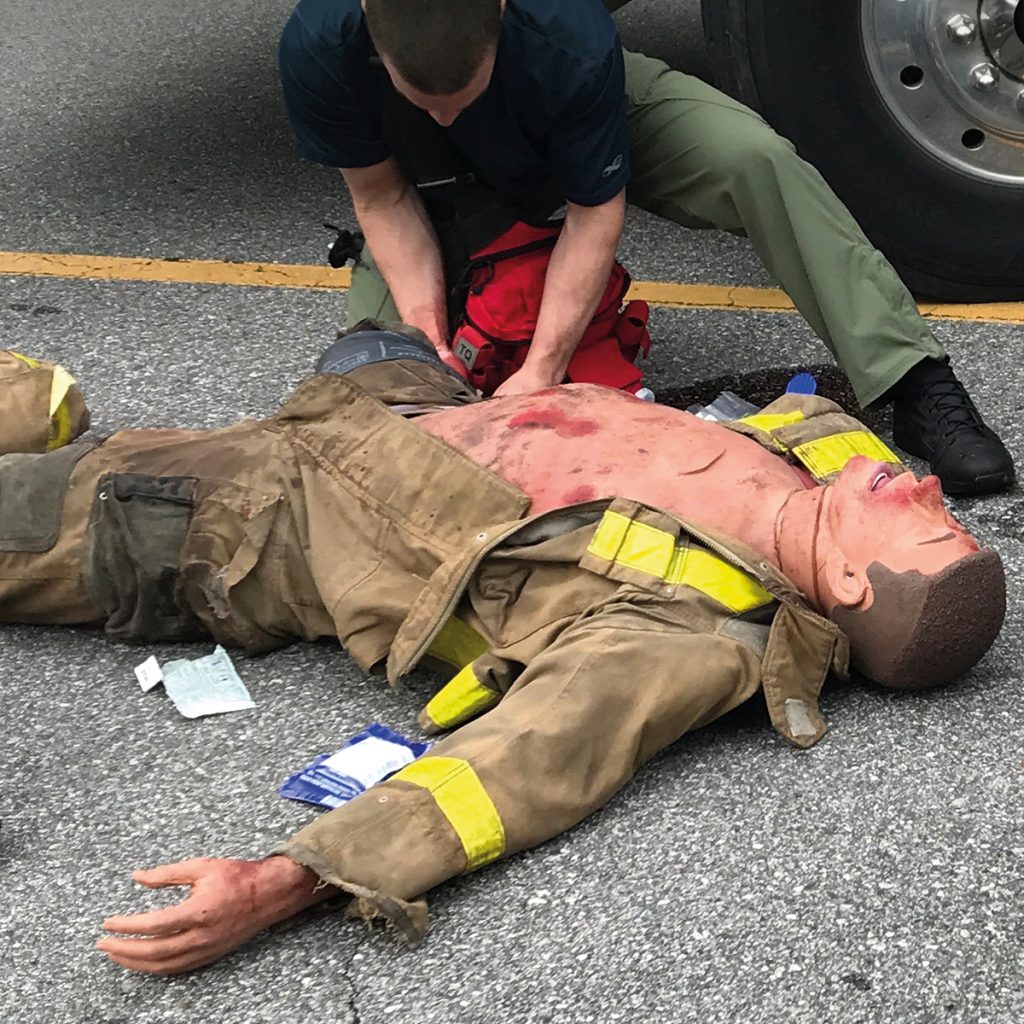
- Capitalizing on operant conditioning, if as an instructor, you provide immediate feedback, you can reinforce the learner’s actions. This feedback can be verbal or tactile, with equipment like high-fidelity manikins. These realistic manikins (many of them have screens) deliver immediate feedback, allowing the learner to correct mistakes and improve performance in real-time.
- Another behaviorism strategy is to employ repetition. When learners get to practice again and again in a simulated environment, they get many chances to associate behaviors and consequences, and are reinforced. And it’s no secret that repetition helps you remember things!
A behaviorist approach can help build technical or psychomotor skills and cause a change in behavior. When the instructor shows specific desired behavior, learners observe the manner in which it must be performed, and then a certain rubric helps evaluate their performance and reinforce them.
