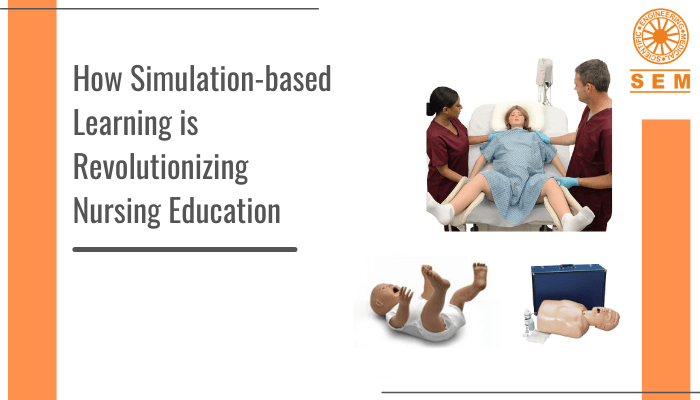
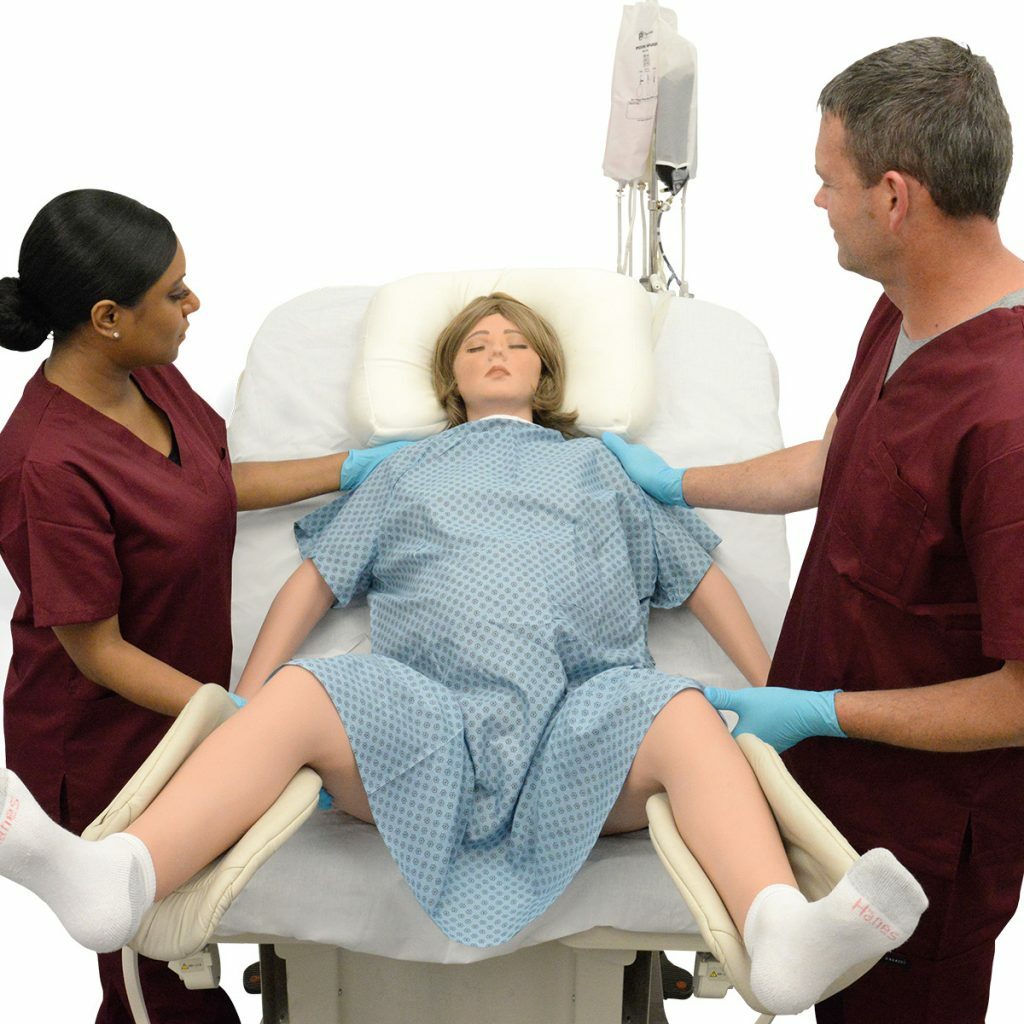
5 Reasons Why Simulation Training is Better | Healthcare
The benefits of incorporating simulation training in teaching specific medical skills are manifold. But what are the 5 biggest advantages that make it a viable option that delivers superior results to using the traditional teaching paradigm alone? Let’s find out.
What is Simulation Training?
Simulation training is the process of reproducing realistic environments and situations (often with the use of lifelike simulators/manikins and trainers/medical skills) to create a hands-on learning experience for a learner to practice certain skills. Simulation has been adopted into various fields as a method of learning. For example, pilots first learn to fly a plane on a simulator. Today, it is an essential teaching tool in various industries like aviation, military, and healthcare.
5 Things that Make it Better than Traditional Learning
There are many more benefits to simulation learning other than the fact that it provides the opportunity for hands-on learning. Here are 5 reasons why it is effective (and better):
It provides a safe environment and avoids risk to real patients
While simulation provides an excellent hands-on learning opportunity (theoretical learning isn’t enough for some skills), it does so in a safe environment. This means that students can explore. That they are free to make mistakes and are given the chance to learn from their mistakes rather than being reprimanded for them or the mistakes translating into real-life blunders. This is a rather important attribute of the learning process- the privilege to be able to make mistakes and learn from them. And when students feel free to explore, they inarguably learn better. On top of that, it means that real patients will not be put at risk, as it is when learners practice on real patients- one mistake and a lot could go wrong. Plus, not everyone is comfortable with being attended by a fresher-simulation also helps avoid that.
It builds team skills (among many others)
Usually, in the real-life clinical setting, professionals don’t work alone. A whole team of individuals and a whole lot of work goes into saving lives. Individuals must work together to make the best decisions possible in time to save a patient’s life and deliver optimal treatment quality. Apart from building skills like decision-making skills and the ability to think on your feet, simulation in healthcare training helps build communication and collaboration skills and the ability to work in a team. It also helps with team leading, team building, and crisis resource management skills. People don’t just start working together if placed in the same room; the ability to work efficiently as part of a team is important.
It builds confidence AND improves the quality of patient care delivered
By bridging the gap between theory and practice, simulation training is able to instill a kind of confidence in learners that enables them to go ahead and deliver excellent quality care as they step into the profession. And confidence is also directly linked to competence. A confident professional will be able to smartly deal with any situation- like when interacting with patients or their families, or when there is a tough decision to make. So when learners start to develop confidence, it becomes easier for them to start taking their own decisions and operating by their own autonomy.
It provides real-time feedback
Not only does simulation training and medical skills bridge the gap between theory and practice, through the use of lifelike simulators and trainers with monitors that display real-time feedback, it is made easier to assess the student’s performance. But this isn’t useful for the instructor alone. It means that the student can evaluate his own performance as he works on the patient (manikin or trainer) and evolve to make better decisions during the process. This is a benefit that is not present with the traditional training method. It is one of the things that makes simulation training so effective in healthcare.
It gives learners an idea of what to expect
While a simulated environment is exciting and comfortable, it also prepares learners for what to expect in a real clinical setting. With high-fidelity simulation, there are some distractions as would be in a real hospital. There may be too much noise, a bad smell, or a number of other big and small disturbances that can easily distract someone working on a critical task and result in serious procedural errors. It can also worsen performance and increase the number of attempts and the amount of time taken to do something. Being exposed to such distractions at an early learning stage can accustom the learner to think on their feet and perform better despite said distractions, effectively preventing serious errors.
With such obvious benefits, simulation training greatly outweighs the performance benefits offered by traditional learning alone, and is an indispensable asset in healthcare education.
Follow us on Social Media :